The code snippet is as follows from openpyxl import load_workbook wb = load_workbook (filename = 'large_filexlsx', use_iterators = True) ws = wbget_sheet_by_name (name = 'big_data') The problem is, I don't know the sheet name, and Sheet1/Sheet2 etc didn't work (returned NoneType object)Select sheets to read by name sheet_name = 'User_info', 'compound' This method requires you to know the sheet names in advance Select all sheets sheet_name = None import pandas as pd df = pdread_excel('usersxlsx', sheet_name = 0,1,2) df = pdread_excel('usersxlsx', sheet_name = 'User_info','compound') df = pdread_excel('usersxlsx', sheet_name = None) # read all sheetsMultiple sheets may be written to by specifying unique sheet_name With all data written to the file it is necessary to save the changes Note that creating an ExcelWriter object with a file name that already exists will result in the contents of the existing file being erased Parameters excel_writer pathlike, filelike, or ExcelWriter object
Excel Formula Get Sheet Name Only Exceljet
Get sheet name in excel python openpyxl
Get sheet name in excel python openpyxl- The create_sheet function can insert sheet at arbitrary position by giving a number to the second argument Without arguments, create_sheet function adds sheet to the end of Workbook in default Get all sheet names To get all sheet names of Workbook, access to sheetnames property in Workbook instance Re How to get the Excel sheet names using OLE object python testcomplete I am using "openpyxl" module, we can get the sheet name (but you have to install openpyxl) import openpyxl def getExcelSheetName () wbo = openpyxlload_workbook ("C\TC_Python\Test1xlsx") wso = wboget_sheet_names () for shname in wso LogMessage (shname)




List All Sheet Names In An Excel Workbook With Without Vba Youtube
Everything is set up to retrieve the Google Sheet we've created earlier and get all the records from it There are 3 ways to open a Google Sheet using Python 1 Open Google Sheet by Name Here, we simply need to input the actual name of the Google Sheet that we created gsheet = gcopen ("my_google_sheet") 2The sheet_name parameter defines the sheet to be read from the excel file When we print the DataFrame object, the output is a twodimensional table It looks similar to an excel sheet records 2 List of Columns Headers of the Excel Sheet We can get the list of column headers using the columns property of the dataframe object # Import `load_workbook` module from `openpyxl` from openpyxl import load_workbook # Load in the workbook wb = load_workbook('testxlsx') # Get sheet names print(wbsheetnames) 'Sheet1', 'Sheet2', 'Sheet3' You see that the code chunk above returns the sheet names of the workbook that you loaded in Python
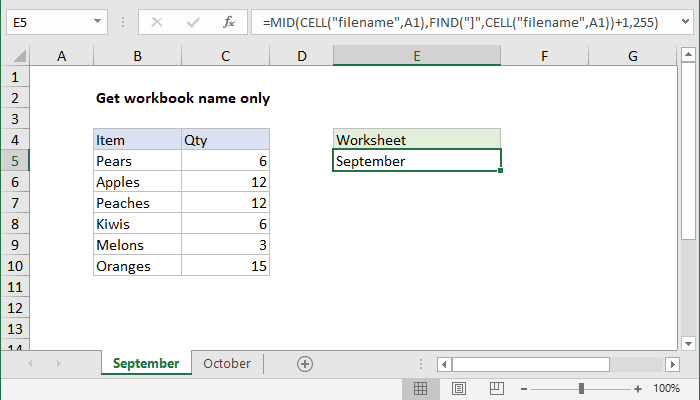
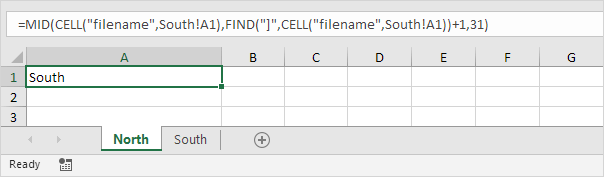
xlsx = pdExcelFile(excel_file) movies_sheets = for sheet in xlsxsheet_names movies_sheetsappend(xlsxparse(sheet)) movies = pdconcat(movies_sheets) If you are reading an Excel file with a lot of sheets and are creating a lot of DataFrames, ExcelFile is more convenient and efficient in comparison to read_excel With ExcelFile, you only need to pass the Excel file once, and then you can use it to getTo get the name of the current worksheet (ie current tab) you can use a formula based on the CELL functionCELL retrieves the workbook name and sheet, and the MID and FIND functions are used to extract just the sheet name In the example shown, the formula in E5 is Provide the file location for the Excel file you want to open in Python wb = load_workbook ('wb1xlsx') In this example, the Excel file is present in the same directory as the python file Hence, there is no need to provide to entire file location Choose the first active sheet present in the workbook using wbactive attribute
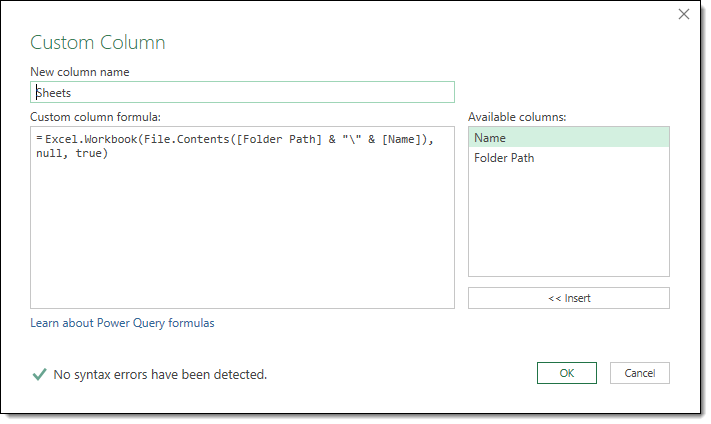
Read Multiple Excel Sheets or Tabs There is no limitation of rows in csv or text file format but in case of excel file, there are only rows allowed in per excel sheet or tab In the below Python code, we are using SQLite to store the data from an excel data file having multiple sheets or tabs As you know that, we can not open this Def get_sheet_details(file_path) sheets = file_name = ospathsplitext(ospathsplit(file_path)1)0 # Make a temporary directory with the file name directory_to_extract_to = ospathjoin(settingsMEDIA_ROOT, file_name) osmkdir(directory_to_extract_to) # Extract the xlsx file as it is just a zip file zip_ref = zipfileZipFile(file_path, 'r') zip_refextractall(directory_to_extract_to) zip_refclose() # Open the workbookxml which is very light and only has meta data, get sheetsTheDef get_sheet_details(file_path) sheets = file_name = ospathsplitext(ospathsplit(file_path)1)0 # Make a temporary directory with the file name directory_to_extract_to = ospathjoin(settingsMEDIA_ROOT, file_name) osmkdir(directory_to_extract_to) # Extract the xlsx file as it is just a zip file zip_ref = zipfileZipFile(file_path, 'r') zip_refextractall(directory_to_extract_to) zip_refclose() # Open the workbookxml which is very light and only has meta data, get sheets




Pandas Read Excel Reading Excel File In Python Journaldev




Pandas Read Excel Reading Excel File In Python Journaldev
To get information about the number of sheets in a workbook, and their names there is a function get_sheet_names( ) This function returns the names of the sheets in a workbook and you can count the names to tell about total number of sheets in current workbook The code will be >>> wbget_sheet_names() 'Sheet1', 'Sheet2', 'Sheet3'From openpyxl import Workbook workbook = Workbook() sheet = workbookactive sheet"A1" = "hello" sheet"B1" = "world!" workbooksave(filename="hello_worldxlsx") The code above should create a file called hello_worldxlsx in the folder you are using to run the codeThe get_worksheet_by_name() method returns the worksheet or chartsheet object with the the given name or None if it isn't found worksheet = workbook get_worksheet_by_name ( 'Sheet1' ) workbookget_default_url_format()




Get Data From Multiple Excel Files With Different Sheet Names Into Power Bi Radacad



How To Get All Sheet Names From All Workbooks In A Folder How To Excel
Def sheet_index (self, sheetname) try sheetnum = self __worksheet_idx_from_name sheetname lower () except KeyError self raise_bad_sheetname (sheetname) return sheetnum def get_sheet_by_name (self, sheetname) sheetnum = self sheet_index (sheetname) return self get_sheet (sheetnum) def get_sheet (self, sheet) if isinstance (sheet To view the list of sheets in an Excel spreadsheet, I can use the xlrd module within the Python script below to obtain the list of worksheets within the workbook #!/usr/bin/python import xlrd as xl file_name = raw_input("File ") workbook = xlopen_workbook(file_name) print workbooksheet_names()There are several Python packages that we can use for writing data to an excel file Here we introduce the Python package xlsxwriter The following example shows how we get data from an excel file and append a new column to the data, then we save the data to a new file




List All Sheet Names In An Excel Workbook With Without Vba Youtube




Working With Excel Sheets In Python Using Openpyxl By Nensi Trambadiya Aubergine Solutions Medium
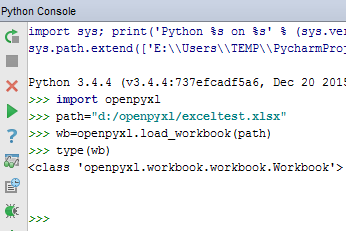
I use the xlrd module in Python scripts to extract data from Excel workbooks You can use the Python xlrd module to list the worksheets in a workbook and you can use the xlrdsheet "visibility" value to determine whether a sheet is hidden and, if it is hidden, whether a user can unhide the sheet The value should be either 0, 1, or 2 with the numbers having the The better way is via Openpyxl, a python module dedicated to working with Excel files It has a method _tables that allows access to defined tables in the spreadsheet #import library from openpyxl import load_workbook #read file wb = load_workbook ( filename ) #access specific sheet ws = wb "Tables"So why not use the power of Python and make your life easy You can make intelligent and thinking Excel sheets, bringing the power of logic and thinking of Python to Excel which is usually static, hence bringing flexibility in Excel and a number of opportunities wso is worksheet object and wbo is workbook object To select a specific sheet we



Python Scripts To Format Data In Microsoft Excel




Merging Spreadsheets With Python Append By Adhaar Sharma Towards Data Science
>>> workbookget_sheet_names() Its better to see the sheet names in our workbook Python provides us the number of sheets with their names without any objection as 'Sheet1', 'Sheet2', 'Sheet3' Up to here, we have loaded an Excel file in memory and checked its sheets Now we refer to the particular sheet we want to delete in this Excel Workbook I want to change the names of these files, based on the document name that's given in cell C5 in each Excelsheet Note the cells C5 E5 are merged I've written the following Python 3 def read_excel_to_dict(file_path, sheet_name) """ Function will open an Excel file at the given sheet, then put the values into a dictionary with the key being the column name The top row in the Excel file is considered the Column Name The top row is only considered a Column if a registry key is set (it normally is by default)



How To Move Data From One Excel File To Another Using Python By Todd Q Brannon The Startup Medium



Use Python Pandas And Openpyxl To Import And Export Excel Sheets And Export Them Back Knime Hub
Xlwings is a Python library that makes it easy to call Python from Excel and vice versa It creates reading and writing to and from Excel using Python easily It can also be modified to act as a Python Server for Excel to synchronously exchange data between Python and Excel Xlwings makes automating Excel with Python easy and can be used for generating an automatic report, creating Excel embedded functions, manipulating Excel There are 2 main ways to export your Python, the first being if you're only exporting 1 sheet, the second being if you're exporting multiple sheets To export 1 sheet, assuming the dataframe name is df, we use the following line of code dfto_excel (r'The Path to where we export the excel file Namexlsx', index = False) #WITH EXPORTED NAME Openpyxl is a Python library used to read and write Excel files (xlsx/xlsm/xltx/xltm files) This module allows the Python programs to read and modify the spreadsheet XLSX file is the default file format for Microsoft Excel It is based on the Office Open XML standard




Openpyxl Python Module To Read Write Excel Files Journaldev



Python Import Excel File Using Pandas Keytodatascience
The Workbook object here represents the Excel file Sheet Names Sheets in Excel consist of columns (with letters starting from A, B, C, etc) and rows (starting from 1, 2, 3, etc) In order to check what sheets we have in our Excel document, we use the get_sheet_names() method as follows excel_documentget_sheet_names() The following line shows a oneliner on how to read an Excel file into memory workbook = xlrdopen_workbook(excel_file) Then, the script iterates through the Excel file's worksheets, one after the other within a for loop The loop includes the following steps Get the worksheet names workbooksheet_names() Extract the data from each worksheetRead Excel files (extensionsxlsx, xls) with Python Pandas To read an excel file as a DataFrame, use the pandas read_excel () method You can read the first sheet, specific sheets, multiple sheets or all sheets Pandas converts this to the DataFrame



Openpyxl Tutorial Read Write Manipulate Xlsx Files In Python Python Excel




Get Data From Multiple Excel Files With Different Sheet Names Into Power Bi Radacad
Examples Reading Excel (xls) Documents Using Python's xlrd In this case, I've finally bookmarked it) from __future__ import print_function from ospath import join, dirname, abspath import xlrd fname = join (dirname (dirname (abspath (__file__))), 'test_data', 'Cad Data Mar 14xlsx') # Open the workbook xl_workbook = xlrdopen_workbookA worksheet object isn't instantiated directly Instead a new worksheet is created by calling the add_worksheet () method from a Workbook () object workbook = xlsxwriterWorkbook('filenamexlsx') worksheet1 = workbookadd_worksheet() worksheet2 = workbookadd_worksheet() worksheet1write('A1', 123) workbookclose() Reading Cell Data When you are working with Microsoft Excel, the data is stored in cells You need a way to access those cells from Python to be able to extract that data OpenPyXL makes this process straightforward Create a new file named workbook_cellspy and add this code to it # workbook_cellspy




Ismail Elkhalouti Medium



Get Sheet Name In Excel Easy Excel Tutorial
In this tutorial, we will see a demonstration on how to use Excel sheets in the python using openpyxl Thanks for reading this article If you like it, click on 👏In the output below the effect of not using any parameters is evident If we don't use the parameter sheet_name we get the default sheet name, 'Sheet1' We can also see that we get a new column in our Excel file containing numbers These are the indices from the dataframe environment setting to an excel workbook (as opposed to a directory or geodatabase), then use the ListTables() function to return a list of sheet names I don't have the code offhand but it'd look




How To Work With Excel Files In Pandas By Dorian Lazar Towards Data Science




Openpyxl Python Module To Read Write Excel Files Journaldev
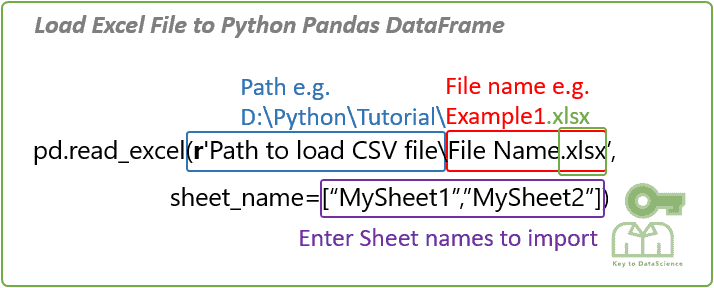
Whereas in Python you need to use thirdparty pip packages to read and write data into the excel files Additionally, we use two libraries to read and write operations into the Excel sheet Firstly, for reading data from the excel file we use xlrd package Pip Home » excel » python – Pandas Looking up the list of sheets in an excel file python – Pandas Looking up the list of sheets in an excel file If you just want to get the sheet names initially, the following function works for xlsx files def get_sheet_details(file_path) sheets = file_name = ospathsplitext(ospathsplit(file And if you have a specific Excel sheet that you'd like to import, you may then apply import pandas as pd df = pdread_excel (r'Path where the Excel file is stored\File namexlsx', sheet_name='your Excel sheet name') print (df) Let's now review an example that includes the data to be imported into Python The Data to be Imported into Python




Get Sheet Name From Excel Page 2 Alteryx Community



How To Search By Worksheet Name In Excel
Now, it is a bit fancier, as the code could be executed with a click On the previous one, I have written quit() , thus one should execute it from the consoleStill, B10 is found Thirdly, I have read a comment from @ashleedawg, that one should be able to use the Excel API and thus use the Find() method from it The whole programming becomes quite easy this way, using the xlwings library Image Create by Author Excel Object Methods The methods in Excel Object Model is the same as the functions in Python, it is callable and performing a taskWriting a function in python shall always end with a pair of parenthesis that holding keywords argument as shown in the Python script below, the function greet end with a pair of parenthesis that holding the argument named "name" import pandas as pd file = 'produceSalesxlsx' data = pdExcelFile(file) print(datasheet_names) #this returns the all the sheets in the excel file 'Sheet1'
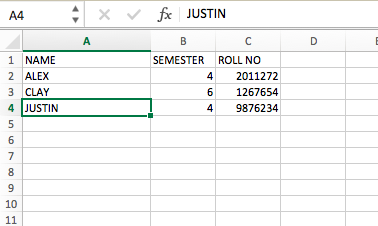



Reading An Excel File Using Python Geeksforgeeks




Obscured Clarity Get Sheet Names From An Excel File Using Java And Poi
Def get_sheet_details(file_path) sheets = file_name = ospathsplitext(ospathsplit(file_path)1)0 # Make a temporary directory with the file name directory_to_extract_to = ospathjoin(settingsMEDIA_ROOT, file_name) osmkdir(directory_to_extract_to) # Extract the xlsx file as it is just a zip file zip_ref = zipfileZipFile(file_path, 'r') zip_refextractall(directory_to_extract_to) zip_refclose() # Open the workbookxml which is very light and only has meta data, get sheets Working with Excel Sheets In this section we will see how we can create more sheets, get name of sheets and even change the name of any given sheet etc 1 Changing the name of an Excel Sheet We can also change the name of a given excel sheet using the title variable Let's see an exampleHere, you'll learn how to use pandas to import Excel spreadsheets and how to list the names of the sheets in any loaded xlsx file Recall from the video that, given an Excel file imported into a variable spreadsheet, you can retrieve a list of the sheet names using the attribute spreadsheetsheet_names Specifically, you'll be loading and checking out the spreadsheet




How To Get The Sheet Name From Excel In Uipath Excelcult




Open Xlsx File Python Specific Sheet Name Code Example
pfread_excel('usersxlsx', sheet_name = 'purchase') means we'll get the 2nd sheet, which is named "purchase" pfread_excel('usersxlsx', sheet_name = 0,2) will return the first and third sheet of the Excel file The returned value is a dictionary of dataframes header If for any reason, data on your Excel sheet doesn't start from Pandas also have support for excel file format We first need to import Pandas and load excel file, and then parse excel file sheets as a Pandas dataframe import pandas as pd excel_file = pdExcelFile ('pandasExxlsx') print(excel_filesheet_names) df = excel_fileparse ('Sheet1') print(df)



How To Use Python Openpyxl To Copy Excel Sheet Data In Same And Different Excel File
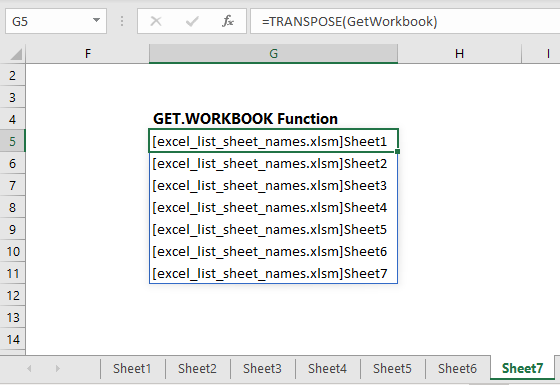



Dynamically List Excel Sheet Names My Online Training Hub




Get Data From Multiple Excel Files With Different Sheet Names Into Power Bi Radacad




Tutorial Python Excel The Definitive Guide Datacamp



Use Openpyxl Create A New Worksheet Change Sheet Property In Python Sou Nan De Gesu




Seven Characters You Can T Use In Worksheet Names Accountingweb
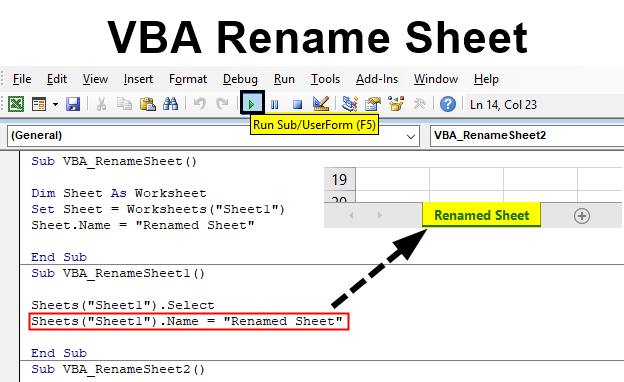



Vba Rename Sheet How To Rename Sheet In Excel Using Vba




A Guide To Excel Spreadsheets In Python With Openpyxl Real Python
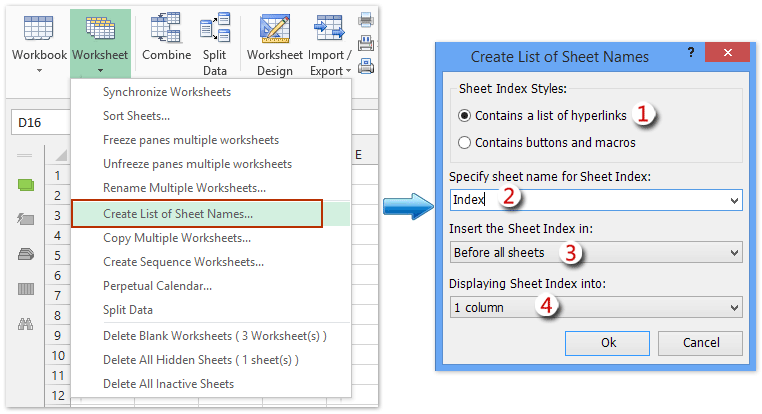



How To Search By Worksheet Name In Excel




Tutorial Python Excel The Definitive Guide Datacamp




How To Use Vba Procedures To Generate A List Of Sheet Names In An Excel Workbook Techrepublic




Your Guide To Reading Excel Xlsx Files In Python
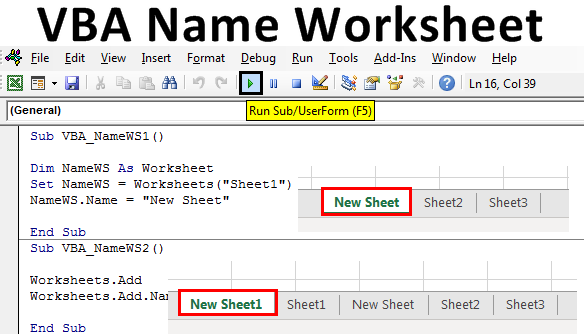



Vba Name Worksheet How To Change Name Of Worksheet In Excel Vba




Get Data From Multiple Excel Files With Different Sheet Names Into Power Bi Radacad




Python Code To Create Sheet Name As A New Column And Merge All The Sheets In Excel Stack Overflow




The Workbook Class Xlsxwriter Documentation
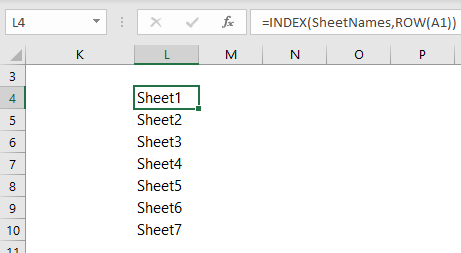



Dynamically List Excel Sheet Names My Online Training Hub




Openpyxl Worksheet Name Jobs Ecityworks
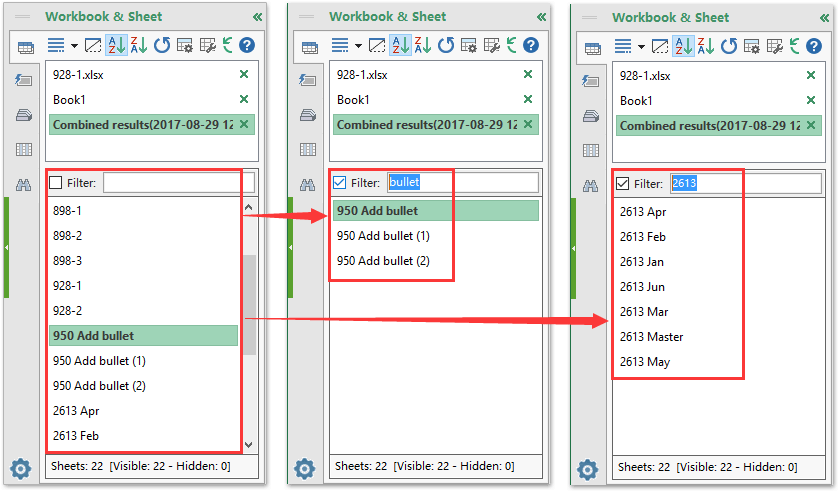



How To Search By Worksheet Name In Excel




How To Move Data From One Excel File To Another Using Python By Todd Q Brannon The Startup Medium
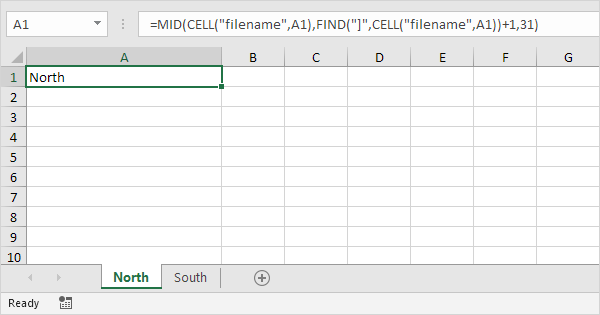



Get Sheet Name In Excel Easy Excel Tutorial




Easily Extract Information From Excel With Python And Pandas Youtube




How To Get The Sheet Name From Excel In Uipath Excelcult




Get Data From Multiple Excel Files With Different Sheet Names Into Power Bi Radacad




Excel Vba Filtering And Copy Pasting To New Sheet Or Workbook




Google Apps Script How To Get The Sheet Name And Spreadsheet Name And Add To A Cell On Google Sheets With A Custom Function Yagisanatode




Read Excel With Python Pandas Python Tutorial




How To Get The Sheet Name In Google Sheets Formula Spreadsheet Point




Solved Include Excel Sheet Name In Output Dataset Using D Alteryx Community




How To Get The Sheet Name From Excel In Uipath Excelcult



Excel Get Sheet Name From Cell
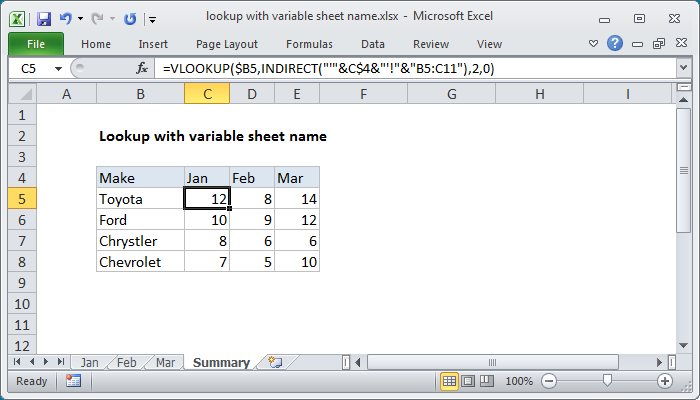



Excel Formula Lookup With Variable Sheet Name Exceljet
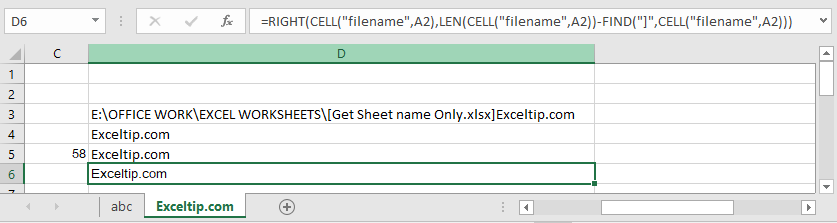



How To Get Sheet Name Of Worksheet In Excel




Excel Formula Get Sheet Name Only Exceljet
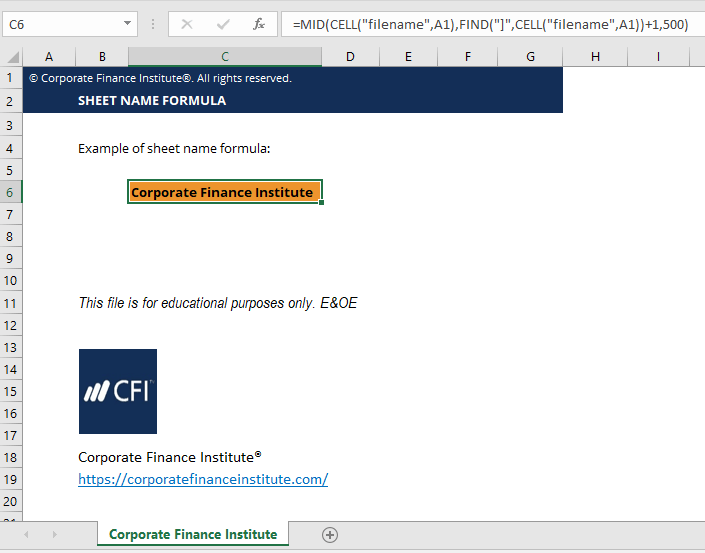



Sheet Name Code Excel Download Template Formula Example
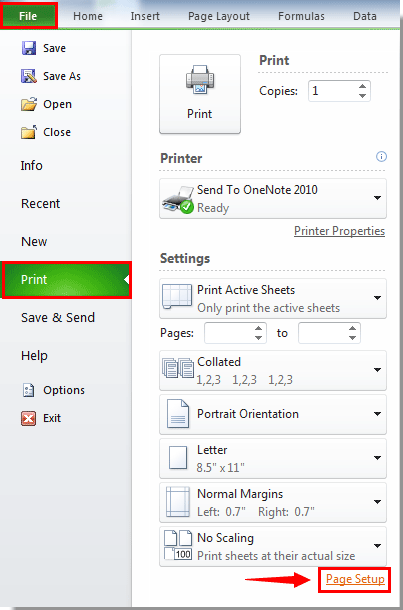



How To Print Sheet Name Or A List Of Sheet Names In Excel




Combine Multiple Excel Worksheets Into A Single Pandas Dataframe Practical Business Python
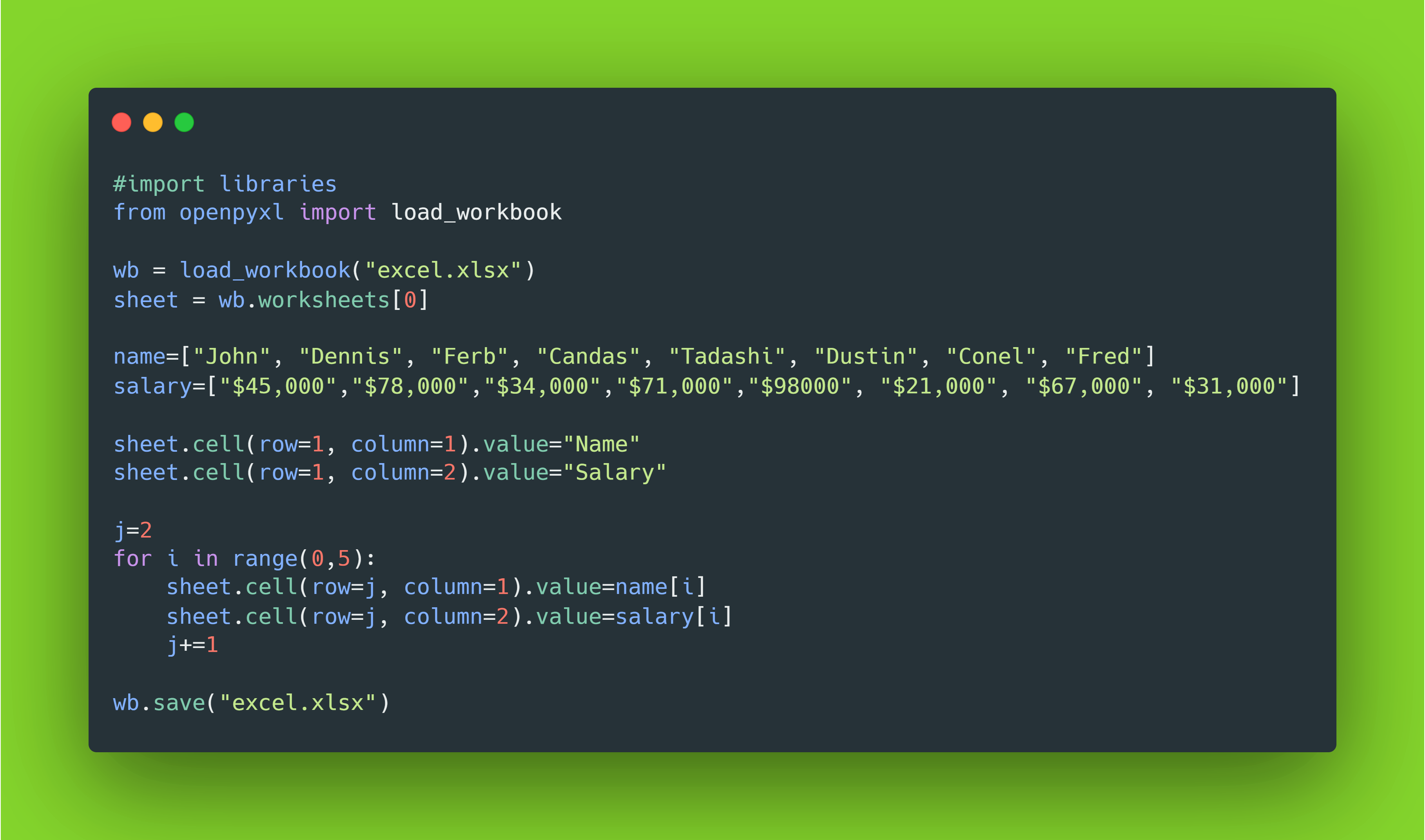



How To Read And Write Excel Files In Python By Haider Imtiaz Python In Plain English
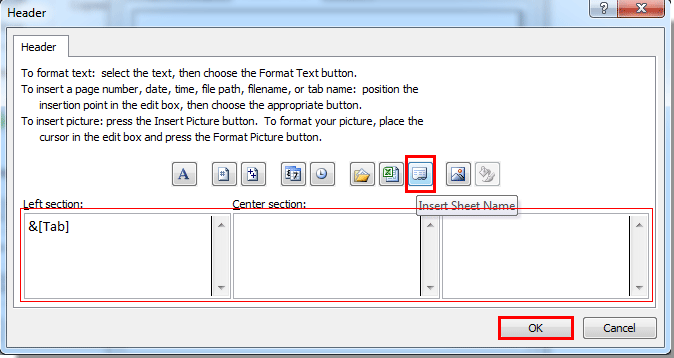



How To Print Sheet Name Or A List Of Sheet Names In Excel
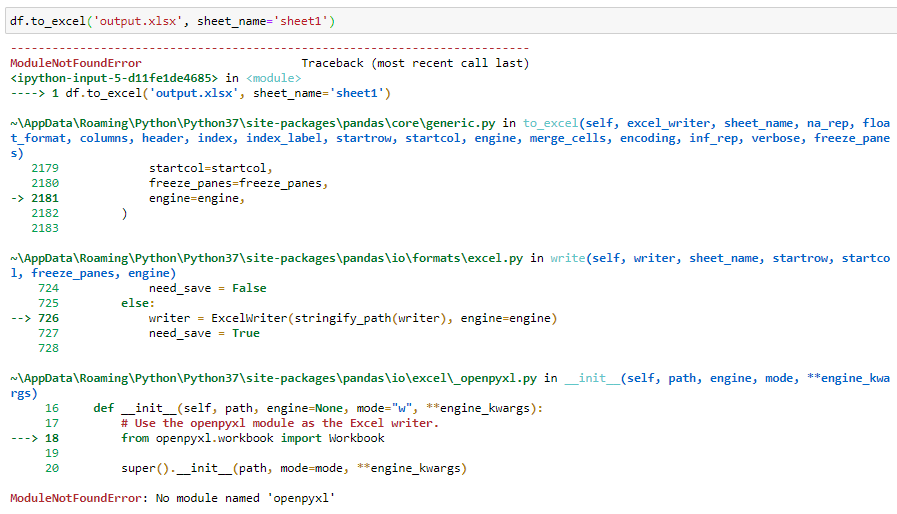



How To Work With Excel Files In Pandas By Dorian Lazar Towards Data Science




Hands On Python Openpyxl Tutorial With Examples




How To Get The Sheet Name In Google Sheets Formula Spreadsheet Point




Get Active Workbook Worksheet Name Path Full Address In Excel Vba




Google Apps Script How To Get The Sheet Name And Spreadsheet Name And Add To A Cell On Google Sheets With A Custom Function Yagisanatode
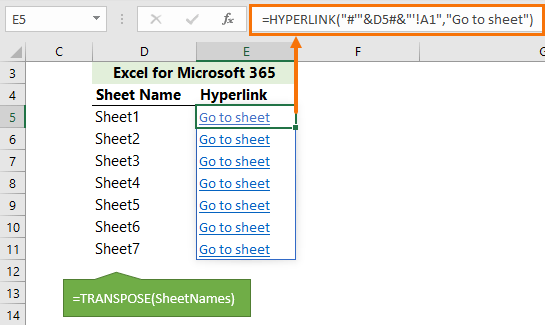



Dynamically List Excel Sheet Names My Online Training Hub




How To Use Vba Procedures To Generate A List Of Sheet Names In An Excel Workbook Techrepublic
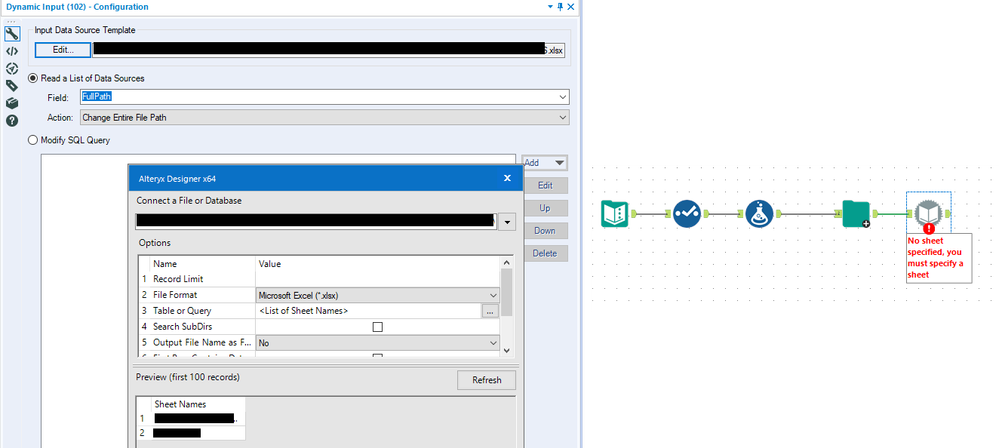



Solved Dynamic Input List Of Excel Sheet Names Alteryx Community




Excel Get Sheet Name By Index



Reading Excel With Python Xlrd Programming Notes




The Workbook Class Xlsxwriter Documentation




How To Read All Sheet Name In Excel Using Pandas Code Example
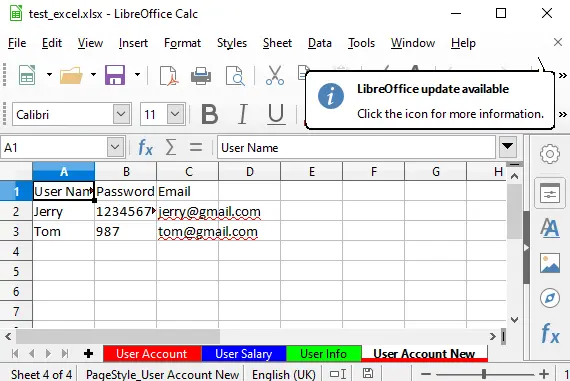



How To Use Python Openpyxl To Copy Excel Sheet Data In Same And Different Excel File



1




Python Implements Reading Data From Excel For Batch Get Requests Programmer Sought



The First Sheet Name Is In A Language Different From The Office Display Language Office Microsoft Docs
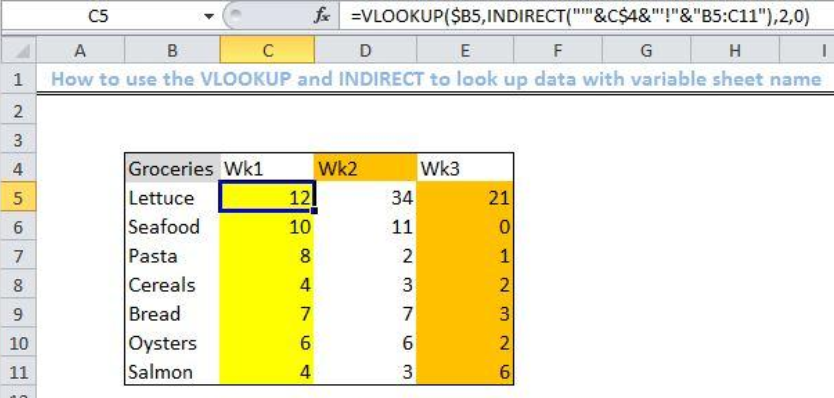



How To Lookup With Variable Sheet Name Excelchat
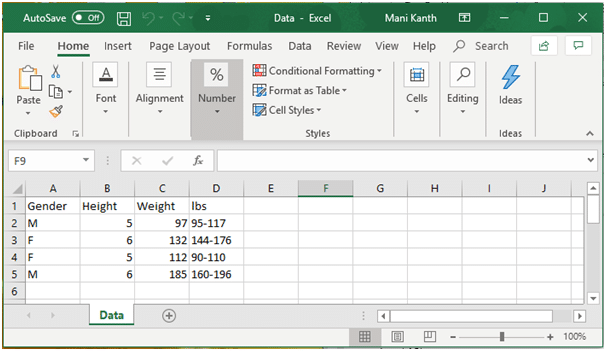



Reading Ms Excel Dataset By Using Pandas Datascience
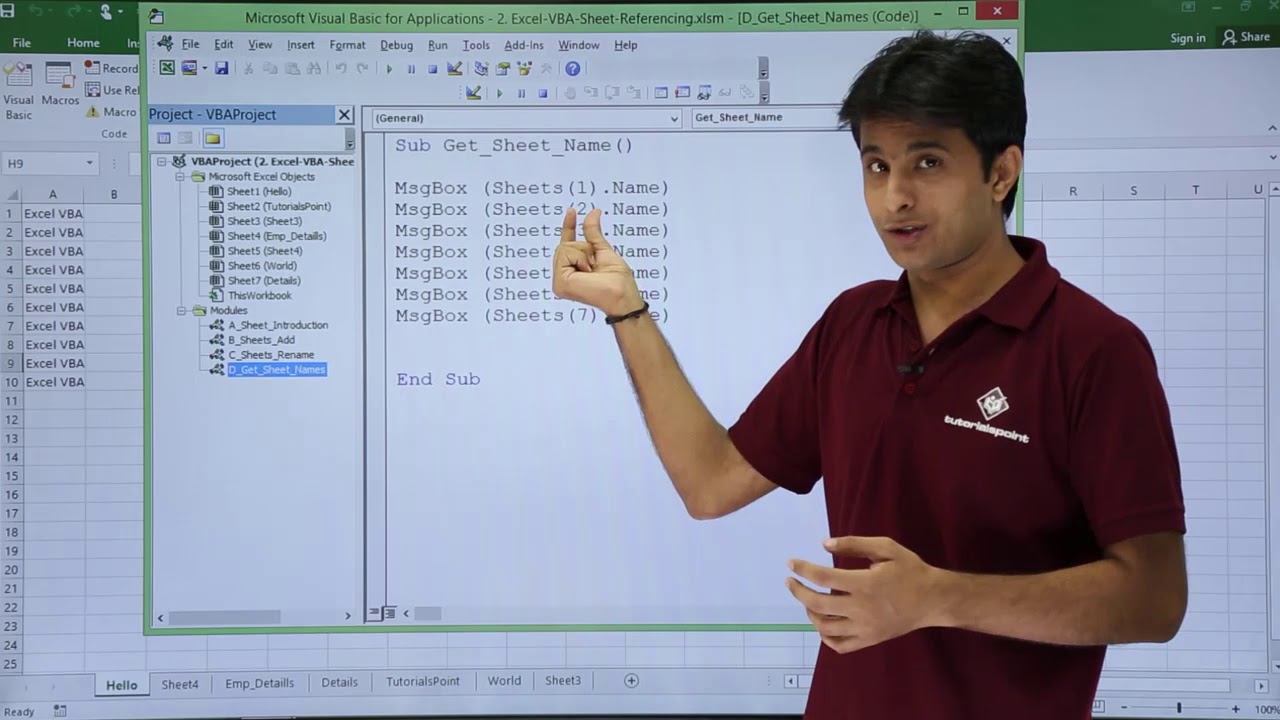



Excel Vba Get Sheet Names Youtube




Excel Formula Get Sheet Name Only Exceljet
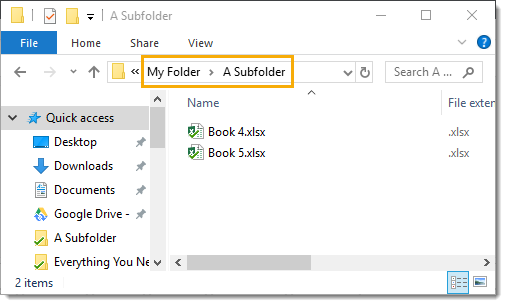



How To Get All Sheet Names From All Workbooks In A Folder How To Excel




Combine Multiple Excel Worksheets Into A Single Pandas Dataframe Practical Business Python




Tutorial Python Excel The Definitive Guide Datacamp




Get Sheet Names In Google Sheets Current Sheet And All Sheets Youtube




Excel Library In Robot Framework
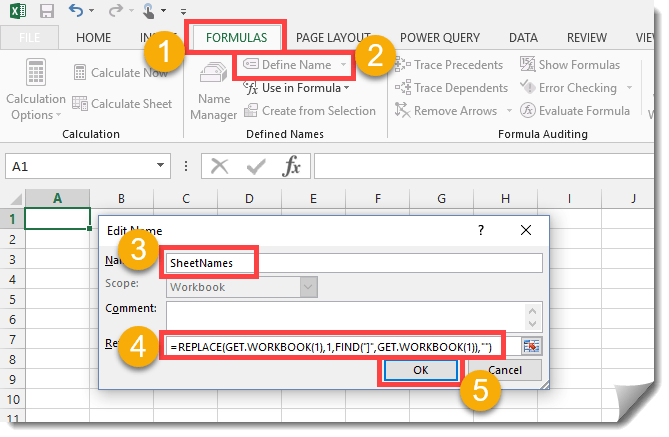



How To Generate A List Of Sheet Names From A Workbook Without Vba How To Excel



How To Get List Of Sheets Names In Google Sheets




Msbi Sql Server And Gcp With Python How To Loop Through A Different Sheets Of A Single Excel Workbook In Ssis



Q Tbn And9gcsfe Rkwmbsvjfe Uyanglrxj Gyyzkapg8qioqgqcxgsehuljh Usqp Cau




Python How To Find Corresponding Values Between An Excel File And A Dataframe Stack Overflow




Solved Listing The List Of Sheet Names From Xls Alteryx Community
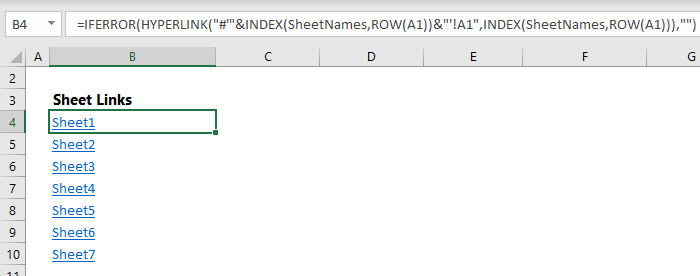



Dynamically List Excel Sheet Names My Online Training Hub
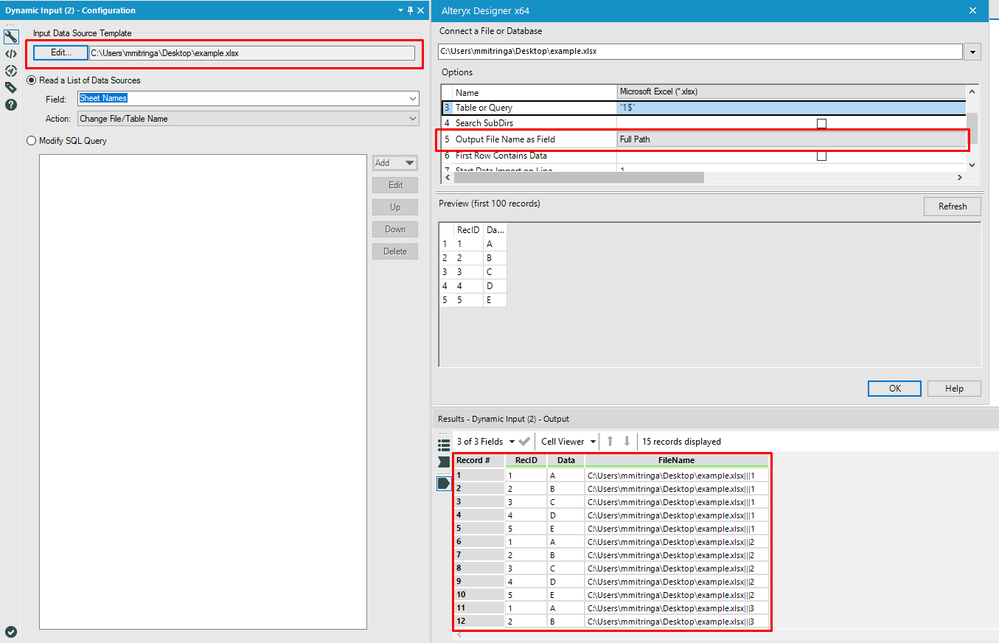



Solved Include Excel Sheet Name In Output Dataset Using D Alteryx Community



1




How To Get All Sheet Names From All Workbooks In A Folder How To Excel



Writing To An Excel Sheet Using Python Geeksforgeeks




Openpyxl Python Module To Read Write Excel Files With Examples All Learning




Google Apps Script How To Get The Sheet Name And Spreadsheet Name And Add To A Cell On Google Sheets With A Custom Function Yagisanatode




Use Openpyxl Create A New Worksheet Change Sheet Property In Python Sou Nan De Gesu



1




Openpyxl Python Module To Read Write Excel Files Journaldev



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿