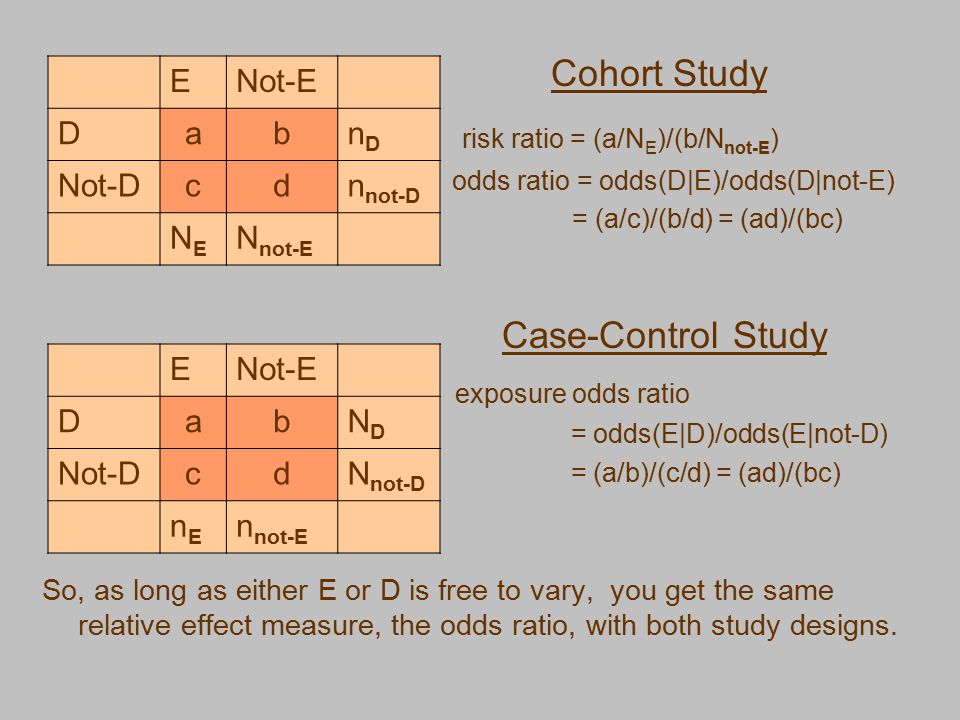
This format is commonly expressed in cohort studies using logistic regression When the incidence of an outcome is low (Sep 02, · The risk or odds ratio is the risk or odds in the exposed group divided by the risk or odds in the control group A risk or odds ratio = 1 indicates no difference between the groups A risk or odds ratio > 1 indicates a heightened probability of the outcome in the treatment group The two metrics track each other, but are not equalAug 07, 14 · Odds ratio vs risk ratio You know the difference between risk and odds A risk is the proportion of subjects with an event in a total group of susceptible subjects Thus, we can calculate the risk of having a heart attack among smokers (infarcted smokers divided by the total number of smokers) and among nonsmokers (the same, but with non

What Is The Difference Between The Risk Ratio Rr And The Odds Ratio Or Quora
Cohort study relative risk vs odds ratio
Cohort study relative risk vs odds ratio-Jan 10, 13 · Odds ratio vs relative risk Odds ratios and relative risks are interpreted in much the same way and if and are much less than and then the odds ratio will be almost the same as the relative risk In some sense the relative risk is a more intuitive measure of effect sizeMay 15, 12 · In case–control studies, the odds ratio is the appropriate effect estimate, and the odds ratio can sometimes be interpreted as a risk ratio or rate ratio depending on the sampling method1 – 4 However, in cohort studies and



Relative Risks And Odds Ratios What S The Difference Mdedge Family Medicine
The relative risk and the odds ratio are measures of association between exposure status and disease outcome in a population Relative risk In epidemiology, relative risk (RR) can give us insights in how much more likely an exposed group is to develop a certain disease in comparison to a nonexposed group Once we know the exposure and disease status of a research population,A value lower than 100 indicates decreased risk The 95% confidence intervals and statisticalJun 02, 10 · Risk Ratios and Odds Ratios for Common Events in Cross‐sectional and Cohort Studies ORs also are reported in cohort and cross‐sectional studies when logistic regression is used to assess the association between the risk factors and an outcome while controlling for confounding variables RR = relative risk
The relative risk is confused by some with the odds ratio and absolute risk Relative risk is the ratio of the probability of an event occurring with an exposure versus the probability of the event occurring without the exposureFeb 01, 18 · 2) Cohort studies will have information about persontime at risk, and so the desired outcomes are often incidence rates, population attributable risk, or risk ratios The odds ratio estimate for rare outcomes will approximately estimate the risk ratio in this design, but it makes more sense to compute the risk ratio directlyHand Frequently, the odds ratio measure is being used instead of the risk ratio or the incidenceproportion ratio in cohort studies or as an estimate for the incidence density ratio in casereferent studies Therefore, the analyses of epidemiologic data have produced biased estimates and the presentation of results has been misleading
Dec 30, 16 · Odds ratio (OR) and risk ratio (RR) are two commonly used measures of association reported in research studies In crosssectional studies, the odds ratio is also referred to as the prevalence odds ratio (POR) when prevalent cases are included, and, instead of the RR, the prevalence ratio (PR) is calculatedMay 14, 21 · The odds ratio (OR) or the ratio of odds of exposure is thus given by a/cb/d (or ad/bc) The odds ratio is generally a good estimate of the relative risk The terms odds ratio and relative risk are in fact interchangeable when used in casecontrol studies Population and hospitalbased casecontrols studiesOct 01, 07 · This study addresses the measures of effect, that is, the measures that are used to compare the frequency of disease (or other outcome) between two groups The measures of effect are generally expressed as relative risks and odds ratios (OR) (relative measures of effect) or as risk difference (absolute measure of effect)



Using Odds Ratio In Case Control Studies Youtube



Relative Risk Wikipedia
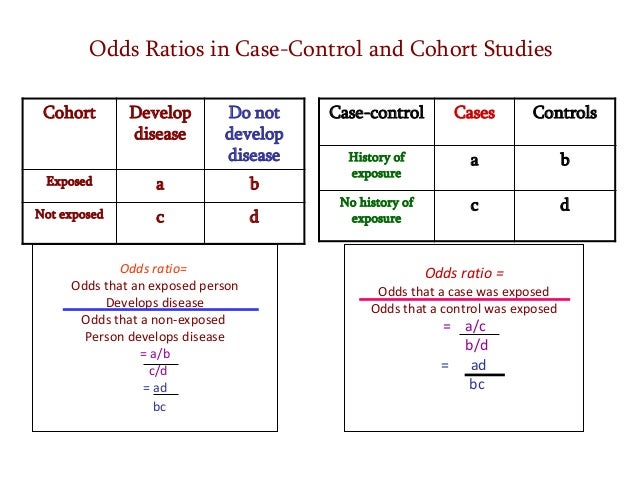
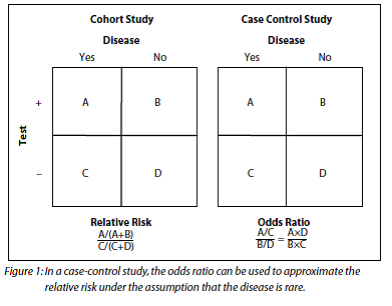
• Odds ratio can be calculated in a cohort study and a casecontrol study • Relative risk can only be calculated in a cohort study Compare the incidence of developing new cases A cohort study follows patients with risk factor (or exposure)Whether the estimates are called odds or risk ratios is a matter of styleJul 02, 08 · When to use the odds ratio or the relative risk?


Estimating Risk



1 The Odds Ratio Relative Odds In A Case Control Study We Do Not Know The Incidence In The Exposed Population Or The Incidence In The Nonexposed Population Ppt Download
Jul 11, 16 · The basic difference is that the odds ratio is a ratio of two odds (yep, it's that obvious) whereas the relative risk is a ratio of two probabilities (The relative risk is also called the risk ratio) Let's look at an example Relative Risk/Risk Ratio Suppose you have a school that wants to test out a new tutoring programIn a control group The odds ratio (OR) is the odds of an event in an experimental group relative to that in a control group An RR or OR of 100 indicates that the risk is comparable in the two groups A value greater than 100 indicates increased risk;Abstract Odds ratios (OR) are commonly reported in the medical literature as the measure of association between exposure and outcome However, it is relative risk that people more intuitively understand as a measure of association Relative risk can be directly determined in a cohort study by calculating a risk ratio (RR)



Relative Risk Or Odds Ratio For Cardiovascular Disease Mortality Download Scientific Diagram


Retrospective Cohort Study Wikiwand
(referent)), not the odds ratio, and it is this inference that becomes troublesome In studies of common outcomes, the estimated odds ratio can, and often does, substantially overestimate the relative risk A method proposed by Zhang and Yu (1) to correct the adjusted odds ratio in cohort studies of common outcomes wasOR 1 − risk ratio In the first formula, the numerator (risk among unvaccinated − risk among vaccinated) is sometimes called the risk difference or excess risk Vaccine efficacy/effectiveness is interpreted as the proportionate reduction in disease among the vaccinated groupMay 04, 09 · Odds ratios approximate risk ratios when outcomes are rare in all noteworthy strata used for an analysis When outcomes are rare, all 4 arguments can be ignored This is most useful in casecontrol studies, in which odds ratios can be interpreted as risk ratios;



1 Relative Risks Odds Ratios Or Hazard Ratios Of Risk Factors For Download Table



A Practical Overview Of Case Control Studies In Clinical Practice Chest
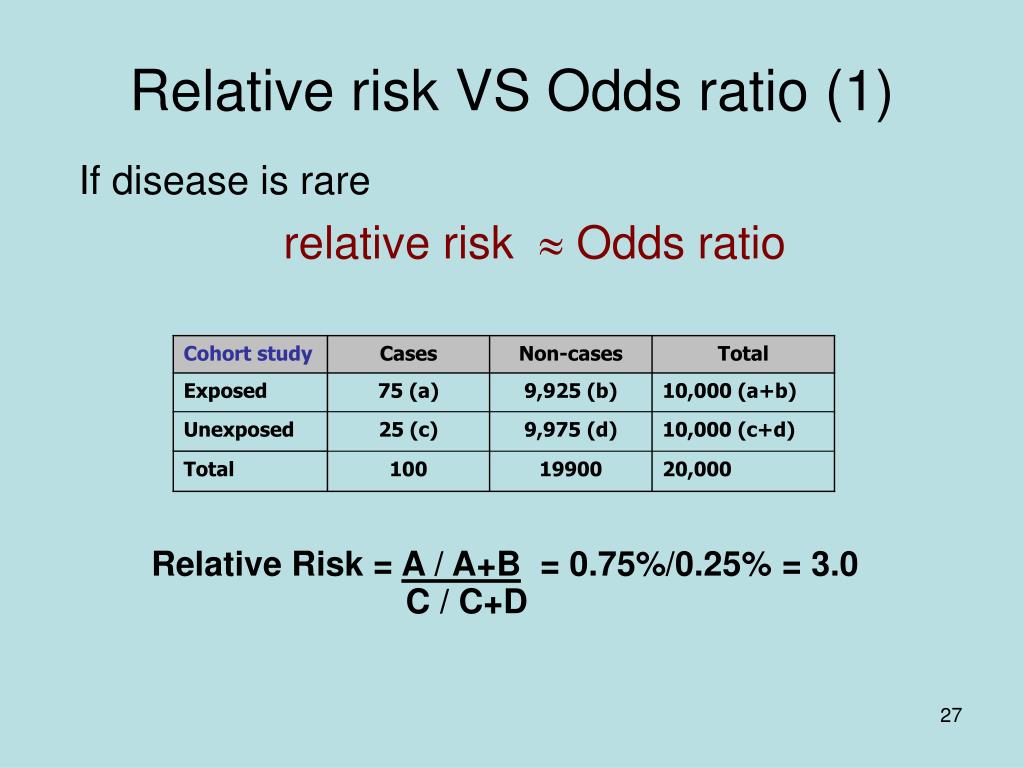
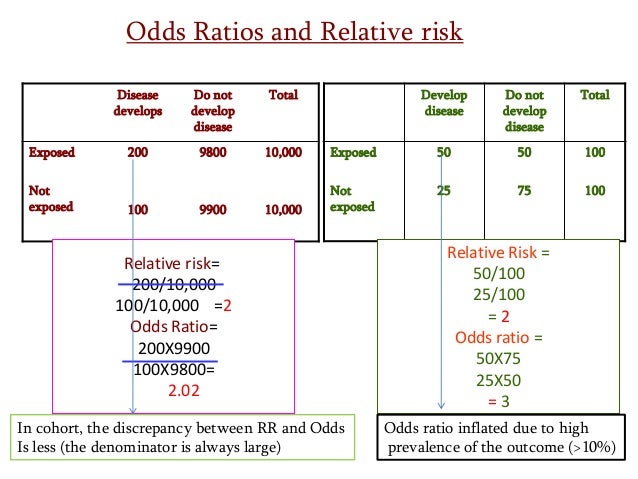
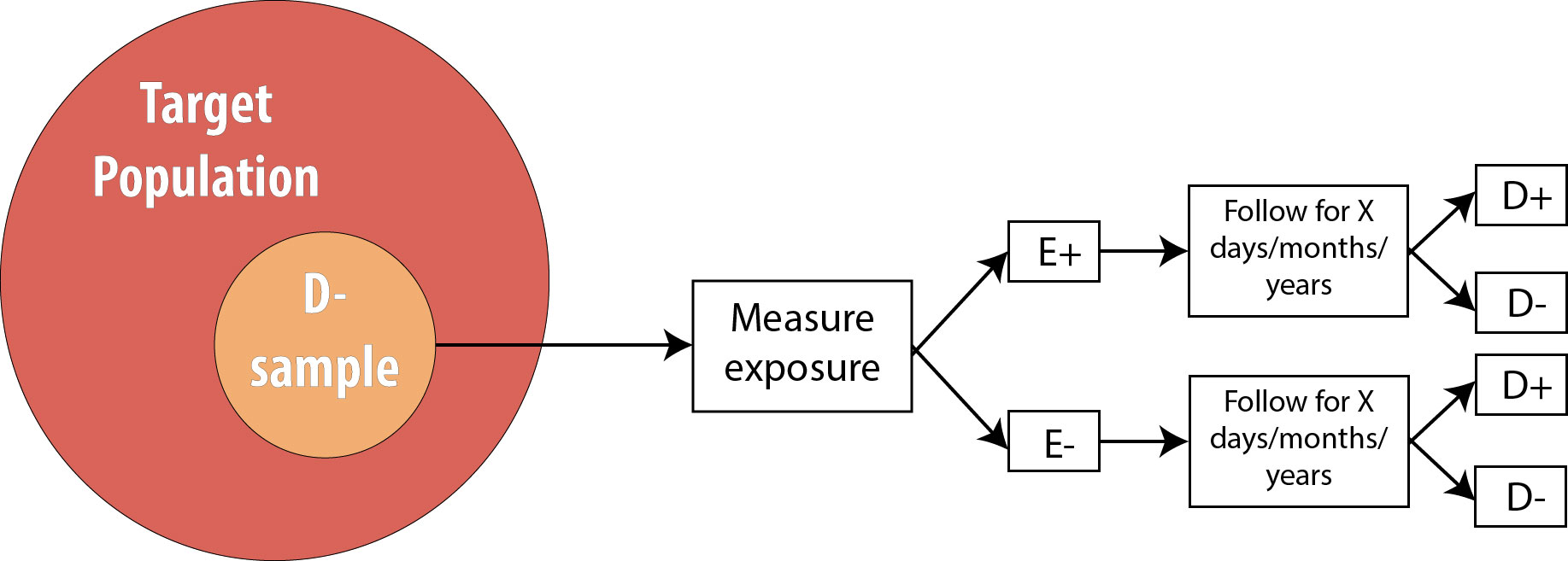
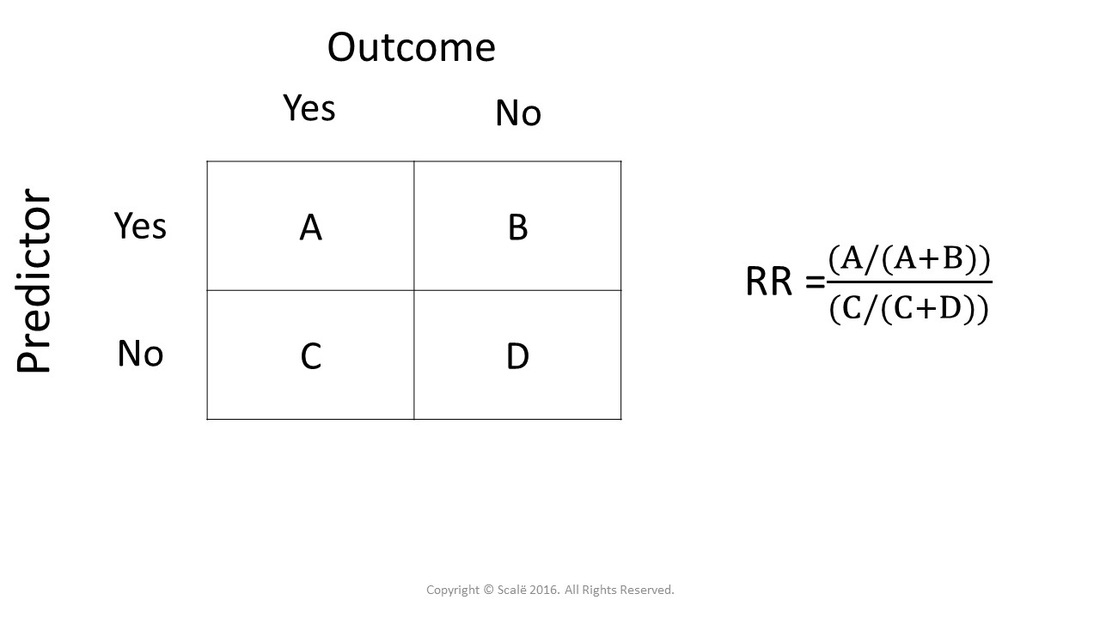
In this study, the risk in the exposed group is 60/0, or 030 cases per person (30 cases per 100 people), and the risk in the unexposed group is 25/0, or 0125 cases per person (13 cases per 100 people) Therefore, the risk ratio is 030/0125, or 24 A risk ratio of 24 implies that the exposed group has 24 times the risk of developingSep 16, 02 · Cases 1 and 4 have the same absolute risk reduction, NNT, and odds ratios, but very different relative risk, relative risk reduction, and risk at baseline Real Example The following example 18 is a prospective study, which compares the incidences of dyskinesia after ropinirole (ROP) or levodopa (LD) in patients with early Parkinson's diseaseMar 19, 18 · The relative risk (or risk ratio) is an intuitive way to compare the risks for the two groups Simply divide the cumulative incidence in exposed group by the cumulative incidence in the unexposed group where CI e is the cumulative incidence in the 'exposed' group and CI u is the cumulative incidence in the 'unexposed' group


Case Control Study Vs Cohort Study Pp Made Easy On Vimeo


Ppt Basic Concept Of Clinical Study Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
Sep 06, 05 · Statistical use and meaning Relative risk is used in the statistical analysis of the data of ecological, cohort, medical and intervention studies, to estimate the strength of the association between exposures (treatments or risk factors) and outcomes Mathematically, it is the expressed as the incidence rate of the outcome in the exposed group, , divided by the outcomeWhen to use the odds ratio or the relative risk?And RR, risk ratio OR=(P 1 /1−P 1)/(P 0 /1−P 0);



Please Fill Out Table 8 Below Using The Results Fr Chegg Com



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1
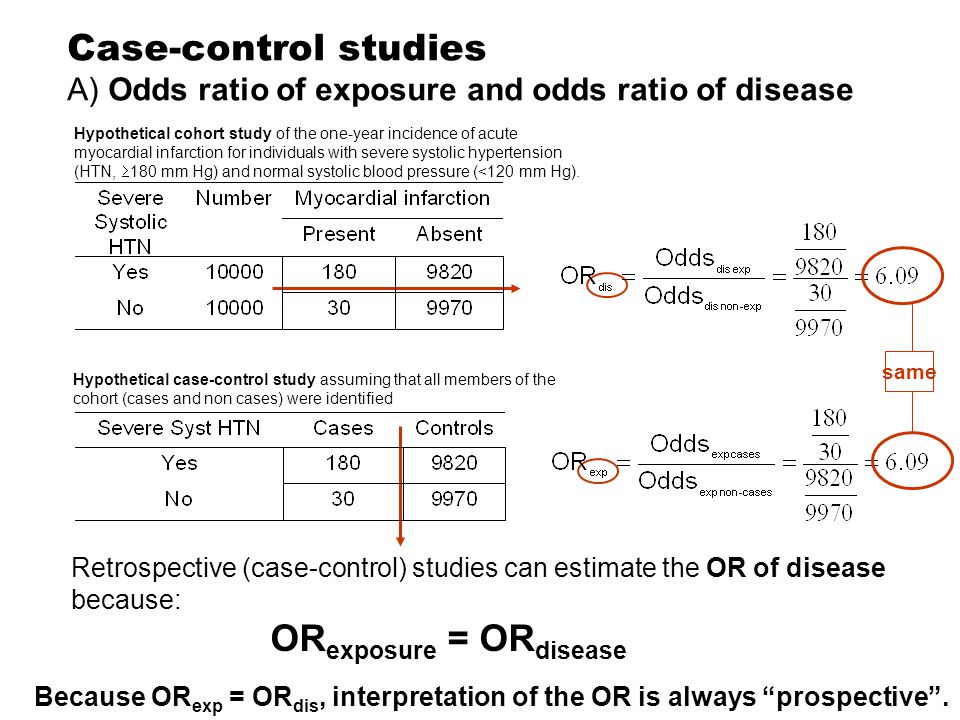
In clinical trials and cohort studies we use relative risk to compare the incidence of health outcomes between groups of differing exposure or treatment For casecontrol trials we use odds ratio to compare the "incidence" of past exposures or treatments Cohort Studies (and clinical trials) –> Relative Risk CaseControl studiesThe Odds Ratio The odds of disease in the exposed group are 7/10, and the odds of disease in the nonexposed group are 6/56 If I compute the odds ratio, I get (7/10) / (5/56) = 656, very close to the risk ratio that I computed from data for the entire population We will consider odds ratios and casecontrol studies in much greater depth inNov 18, 1998 · In a cohort study, P 0 indicates the incidence of the outcome of interest in the nonexposed group and P 1 in the exposed group;



16 Casecontrol Odds Ratios Casecontrol Studies Get Around



Ppt Measures Of Association Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
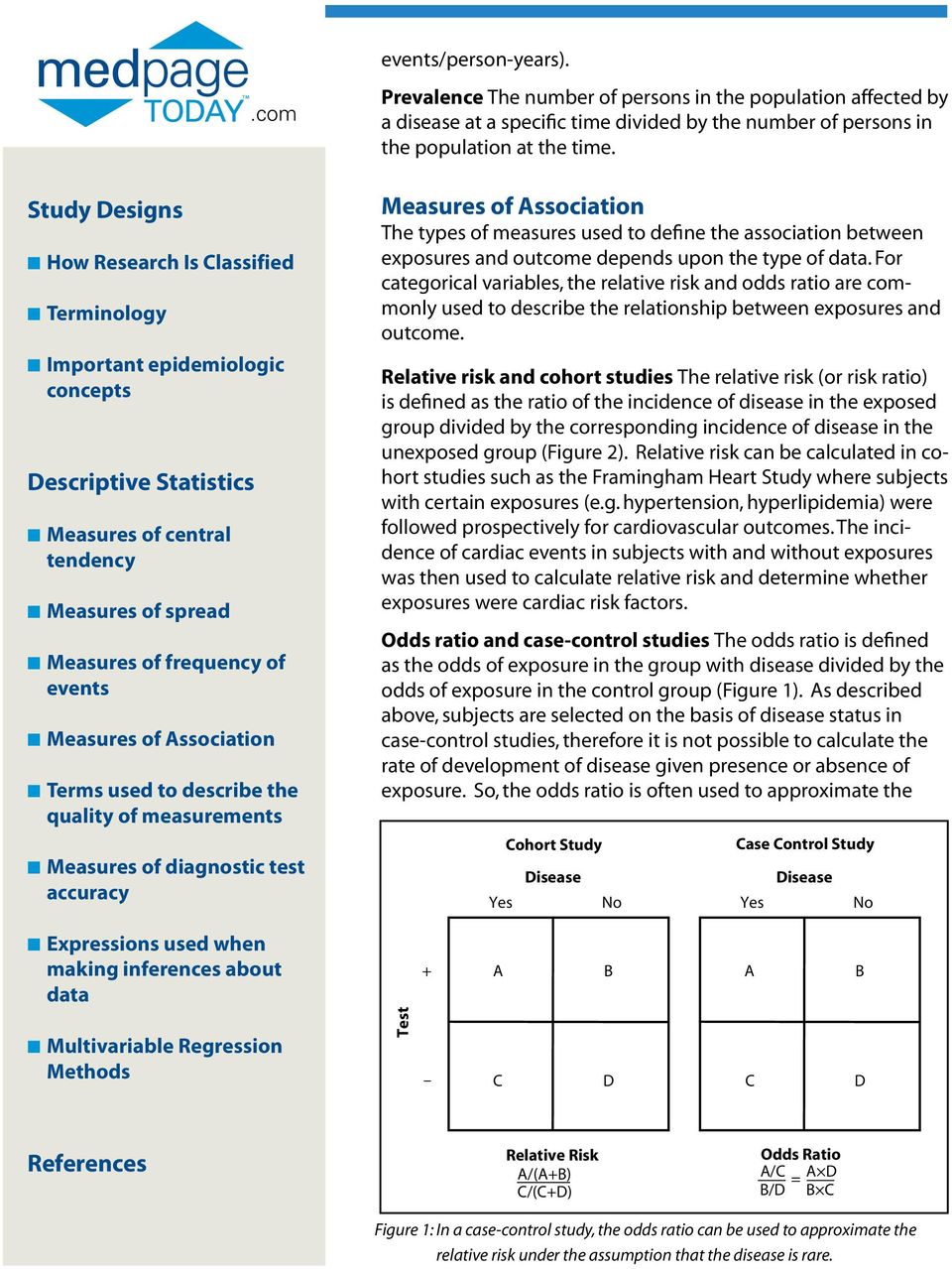
In epidemiological terms, the odds ratio is used as a point estimate of the relative risk in retrospective studies Odds ratio is the key statistic for most casecontrol studies In prospective studies, Attributable risk or risk difference is used to quantify risk in the exposed group that is attributable to the exposure In retrospective studies, attributable risk can not be calculated directly but population attributable riskWhen used for cohort studies and randomized clinical trials, the odds ratio is often incorrectly interpreted as the risk ratio;Apr 06, 10 · Here's the key Relative Risk looks to the future for the effect of a particular cause hence it is used in prospective studies say a cohort study Lets compare the above with Odds Ratio The Odds Ratio can be addressed by asking te following question How many times more likely is a diseased group to have been exposed to a risk factor as



Figure 1 From Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors Ssris And The Risk Of Congenital Heart Defects A Meta Analysis Of Prospective Cohort Studies Semantic Scholar



Relative Risks And Odds Ratios What S The Difference Mdedge Family Medicine
Odds Ratio versus Relative Risk Odds ratio can be calculated in a cohort study and in a casecontrol study − The exposure odds ratio is equal to the disease odds ratio Relative risk can only be calculated in a cohort studyAbout Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us CreatorsCarsten Oliver Schmidt 1 & Thomas


3 5 Bias Confounding And Effect Modification Stat 507


9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 Review Odds Ratios Are Calculated From Case Control Studies Which Are Described On Slide 14 Odds Ratios Are Only Estimates Of Relative Risks Since True Incidence Rates Cannot Be
RR and OR are commonly used measures of association in observational studies In this video I will discuss how to interpret them and how to apply them to patThus, (P 1 /P 0)=OR/(1−P 0)(P 0 ×OR) Since RR=P 1The quote surely just means to say that the odds ratio is a relative risk measure rather than an estimate of the relative risk, which as already point out is only approximately the case in cohort studies/randomized trials for very low proportions By relative risk measure I mean something that is given relative to some comparison group in a way that the absolute difference depends on the



Risk Differences And Rate Differences



Sleep Apnoea Hypertension And Vascular Disease Where Are We Now European Respiratory Society
Oct 27, 11 · Davies et al (1) state that the odds ratio is a common measure in casecontrol studies, cohort studies, or clinical trails Unfortunately, this first sentence of their article is not correct For different study designs, OR should only be used as a measure of effect size when RR can not be estimated directlyBoth the relative risk and odds ratio are relevant in retrospective cohort studies, but only the odds ratio can be used in casecontrol studies Although most casecontrol studies are retrospective, they can also be prospective when the researcher still enrolls participants based on the occurrence of a disease as new cases occurRelative Risk and Odds Ratio for the obese 3) Overall, you can see that decreasing the baseline incidence will decrease the odds ratio (300 in those who are nonobese versus 129 in those who are obese) Obviously, these results run counter to expected results, putting the onus on the researcher to justify them Similarly, you should find



What Is The Difference Between The Risk Ratio Rr And The Odds Ratio Or Quora



Relative Risk Http Www Slideshare Net Terryshaneyfelt7 What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean Study Skills Research Methods Study Tips
May 18, 12 · A risk ratio of 10 indicates identical risk among the two groups A risk ratio greater than 10 indicates an increased risk for the group in the numerator, usually the exposed group A risk ratio less than 10 indicates a decreased risk for the exposed group, indicating that perhaps exposure actually protects against disease occurrenceThe odds ratio then provides an overestimation of the risk ratio, especially when the outcome is frequent The use of logistic regression to adjust for confounding is one of the reasons that odds ratios are presentedDownload PDF Download PDF Hints & Kinks;



Reporting The Results Sage Research Methods


Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1
Casecontrol studies can not calculate incidences or prevalences They can, however, calculate exposure odds ratios 2 1 1 2 A B AB ˆOR = This statistic, which is just the crossproduct ratio of the entries in the 2by2 table, is an estimate of the relative incidence (relative risk) of the outcome associated with exposure9222 Measures of relative effect the risk ratio and odds ratio Measures of relative effect express the outcome in one group relative to that in the other The risk ratio (or relative risk) is the ratio of the risk of an event in the two groups, whereas the odds ratio is the ratio of the odds of an event (see Box 92a)For both measures a value of 1 indicates that the estimated effectsPublished 02 July 08;


Estimating Risk



Odds Ratios And Risk Ratios Youtube
Oct 03, 11 · Given that this is a cohort study, the relative risk (RR) should have been calculated instead of the odds ratio Odds ratios frequently generate larger differences between exposed and nonexposed groups (especially when dealing with nonrare events), therefore overestimating the observed effect (4)



Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios



Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios


How To Be Awesome At Biostatistics And Literature Evaluation Part Ii Tl Dr Pharmacy



Moving Beyond Odds Ratios Estimating And Presenting Absolute


Measures Of Association Ppt Download



Related Image Cross Sectional Study Odds Risk



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1


Absolute Risk Vs Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio Pp Made Easy In Population Perspective Made Easy On Vimeo



Phs 2101 Lecture Notes Summer 19 Lecture 4 Relative Risk Cohort Study Odds Ratio



Learning And Applying Biostatistics How The Guinness Brewery



Ppt The Odds Ratio Relative Odds Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 6056


Introduction To 2 X 2 Tables Epidemiologic Study Design And Measures Of Association Foundations Of Epidemiology



Relative And Atribute Risk



6 Lecture Summary Functional Human Anatomy Murdoch Studocu



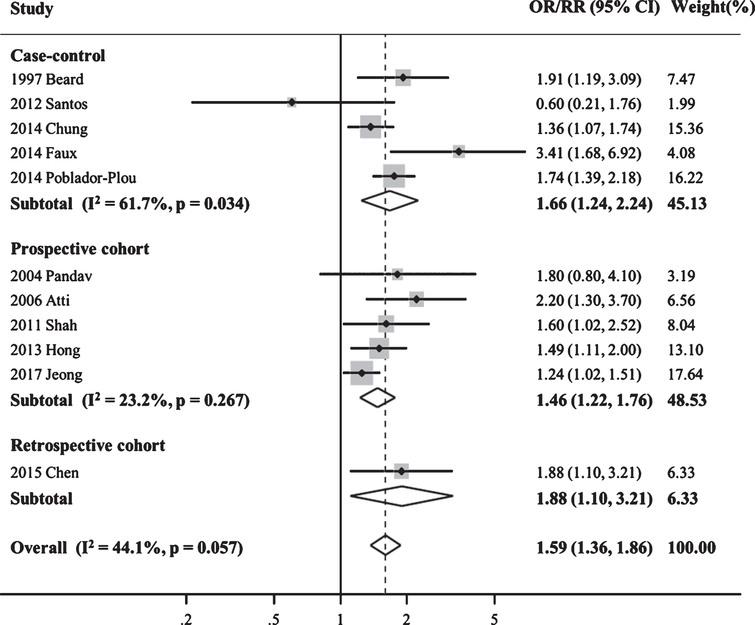
Forest Plot Of Relative Risks And Odds Ratios Of Lung Cancer Associated Download Scientific Diagram


Case Control Studies Statistical Analysis Ppt Video Online Download



The Difference Between Relative Risk And Odds Ratios The Analysis Factor



Relative Risk Or Odds Ratio For Cardiovascular Disease Incidence Download Scientific Diagram



Ppt Measures Of Association Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id


Case Control Study Odds Ratio Relative Risk Best Custom Academic Essay Writing Help Writing Services Uk Online Homeworknowcomlink Web Fc2 Com


Calculate Relative Risk With 95 Confidence Intervals



Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat Sciencedirect


Guide To Biostatistics Pdf Free Download



Chapter 6 Choosing Effect Measures And Computing Estimates Of Effect Cochrane Training


Anemia In Association With Cognitive Impairment A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis Ios Press



Solved The Following Results Were Obtained In An Occupati Chegg Com
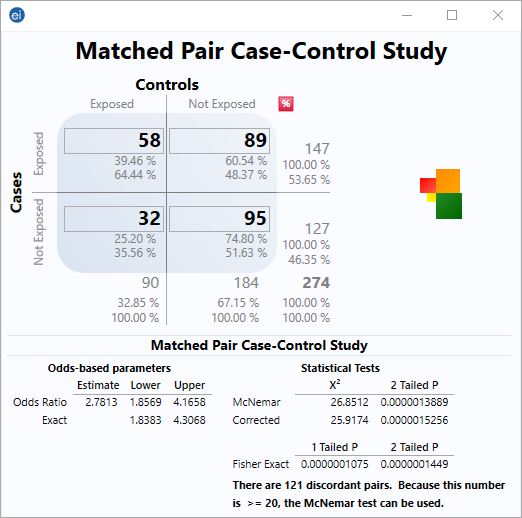


Matched Pair Case Control Statcalc User Guide Support Epi Info Cdc
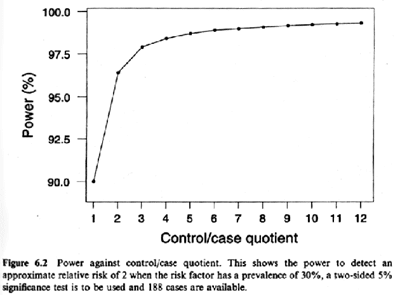


Lesson 9 Cohort Study Design Sample Size And Power Considerations For Epidemiologic Studies



Analytical Studies Note Cohort Study Gives Incidence Relative Risk A R P A R Natural History Of Disease Cohort Study Case Control Study Study



Society For Birth Defects Research And Prevention



Comparison Of Three Methods For Estimating Relative Risk In A Cohort Download Table



Tutorial 5 Answer Odds Ratio Relative Risk



Tablas De Contingencia By Eric Jimenez Issuu
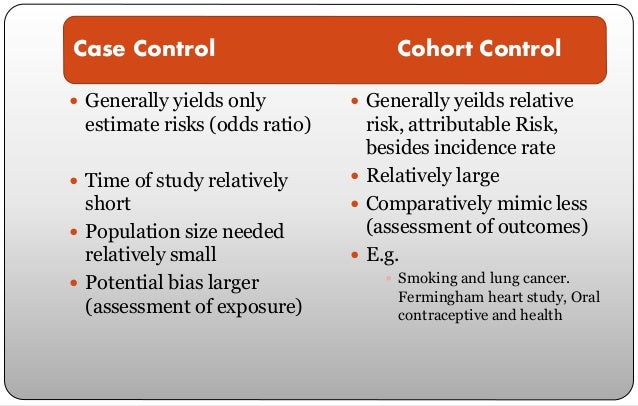


Cohort And Case Con Revised



Tablas De Contingencia By Eric Jimenez Issuu



Study Design Comparison Cohort Study Relative Risk



Measures Of Disease Association Ppt Download



Estimating Risk



How To Interpret And Use A Relative Risk And An Odds Ratio Youtube



Research Techniques Made Simple Interpreting Measures Of Association In Clinical Research Sciencedirect



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1
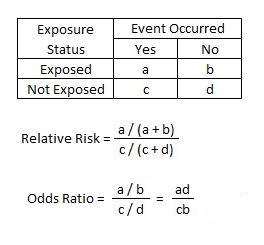


Relative Risk Article
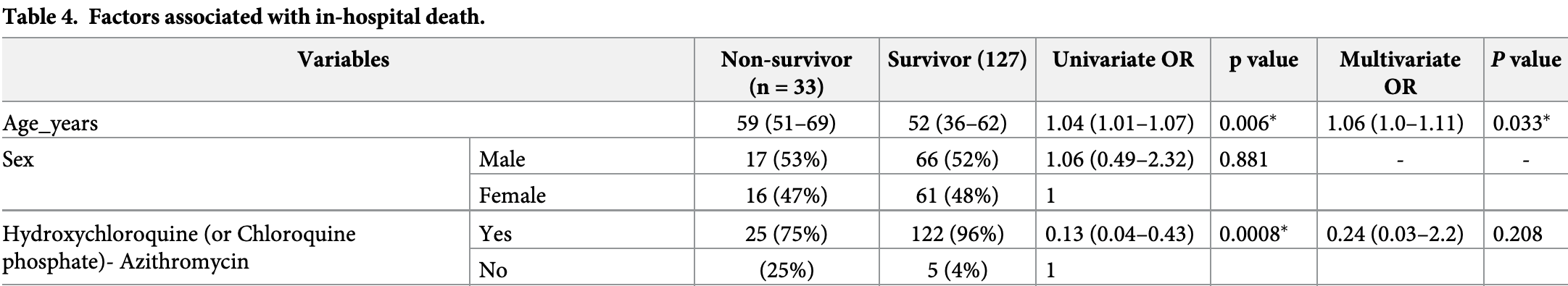


Clinical Characteristics Of Covid 19 Patients Hospitalized At Clinique Ngaliema A Public Hospital In Kinshasa In The Democratic Republic Of Congo A Retrospective Cohort Study



Risks Of And Risk Factors For Covid 19 Disease In People With Diabetes A Cohort Study Of The Total Population Of Scotland The Lancet Diabetes Endocrinology


Plos One Bleeding Risk With Long Term Low Dose Aspirin A Systematic Review Of Observational Studies


Icare An R Package To Build Validate And Apply Absolute Risk Models



Relative Risk Or Odds Ratio For Coronary Artery Disease Mortality Download Scientific Diagram



Ch 12 Relative Risk Rr Or Flashcards Quizlet



Frontiers Odds Ratio Or Prevalence Ratio An Overview Of Reported Statistical Methods And Appropriateness Of Interpretations In Cross Sectional Studies With Dichotomous Outcomes In Veterinary Medicine Veterinary Science



Lecture 08 Strategies For Data Analysis Cohort And Case Control Studies Ppt Relative Risk Cohort Study
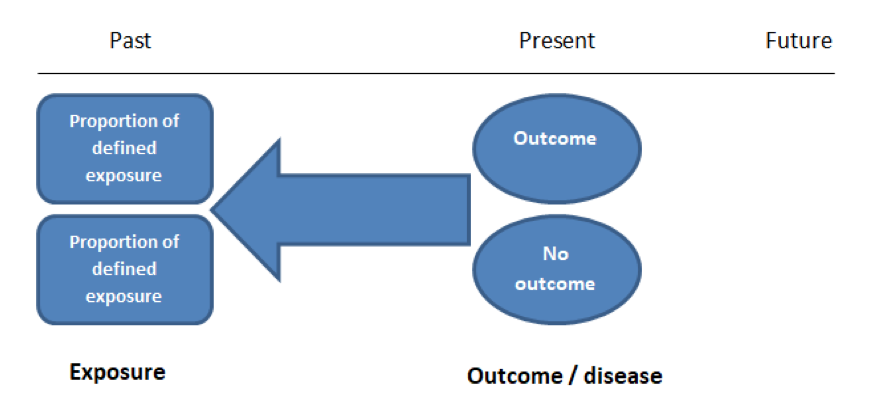


Case Control And Cohort Studies A Brief Overview Students 4 Best Evidence
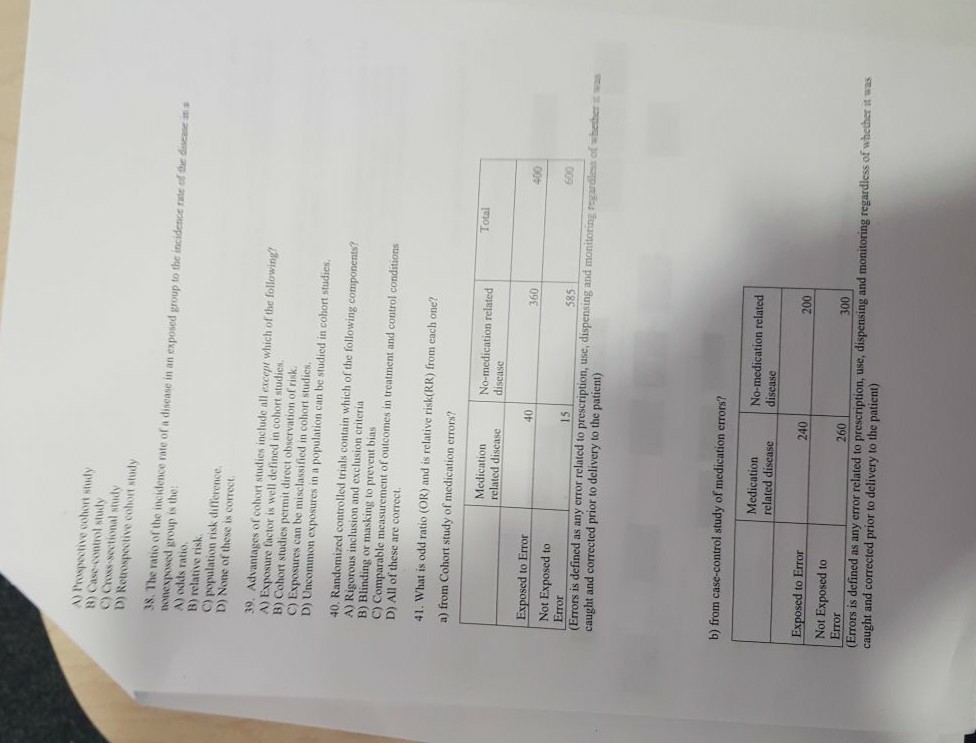


Solved A Prospoctive Cohort Study B Case Control Study Chegg Com



Relative Risk And Absolute Risk Definition And Examples Statistics How To



Calculation Of Relative Risks Rr And Odd Ratios Or Download Table



Abdullah Kharbosh What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean By Ebmteacher Casecontrol Cohort T Co Shfiaepl57 عبر Slideshare



Believability Of Relative Risks And Odds Ratios In Abstracts Cross Sectional Study The Bmj



Figure 2 From Secondhand Smoke Exposure And Risk Of Lung Cancer In Japan A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis Of Epidemiologic Studies Semantic Scholar



Relative Risk Odds Ratios Youtube



Measures Of Association Ppt Download



Relative Risk Wikipedia



Related Image Cross Sectional Study Hazard Ratio Odds



Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat Sciencedirect



Relative Risk And Odds Ratio Usmle The Journey



Calculate Relative Risk With 95 Confidence Intervals



Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk



Relative And Atribute Risk



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿